Planning and Design
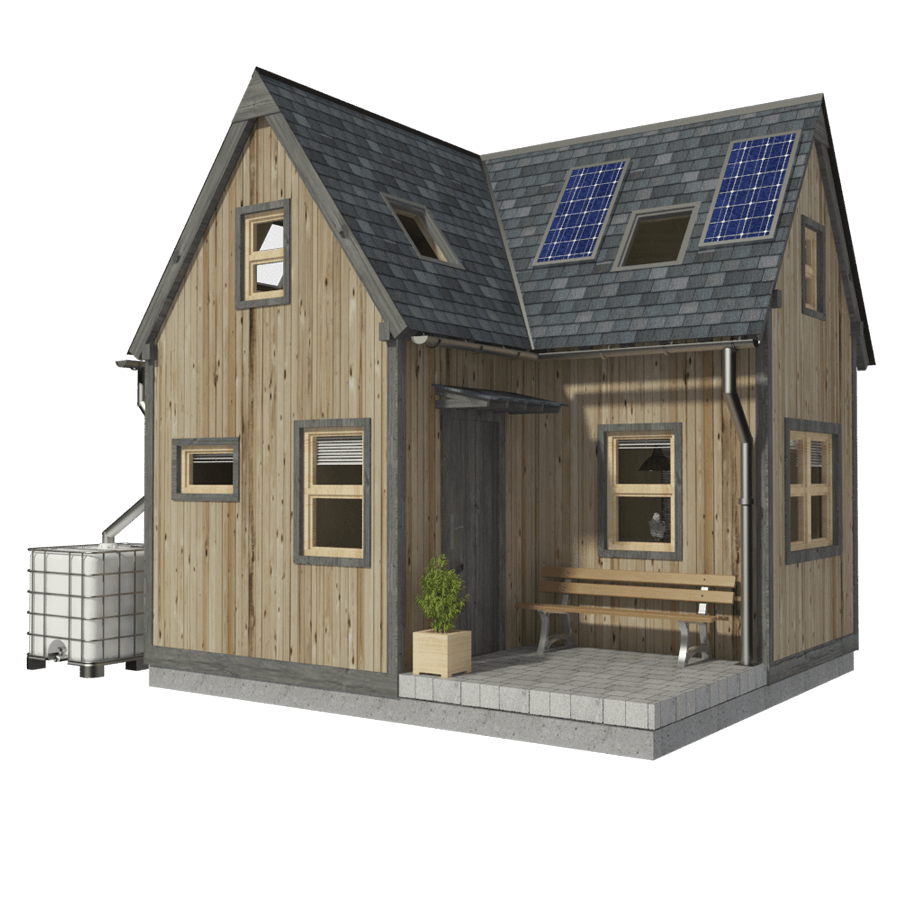
Building a tiny house, especially a 2-bedroom one, requires careful planning and design to maximize space and functionality. This section will guide you through the essential aspects of planning and designing your tiny house.
Design a Floor Plan
A well-designed floor plan is crucial for a comfortable and functional tiny house. The layout should prioritize space efficiency and accommodate the needs of the occupants. Here are some key considerations:
* Living Space: The living space should be open and inviting, offering a comfortable area for relaxing and socializing. Consider a multi-functional sofa that can convert into a bed for guests or additional sleeping arrangements.
* Kitchen: The kitchen should be compact yet functional, with ample counter space and storage. Consider incorporating a small island or peninsula for additional work space and seating.
* Bedrooms: Two bedrooms in a tiny house present a unique challenge. Consider utilizing lofted spaces for bedrooms to maximize floor space. Ensure adequate headroom and proper ventilation in lofted areas.
* Bathroom: The bathroom should be compact but functional, with a shower, toilet, and sink. Consider using space-saving fixtures and a shower curtain to optimize space.
Choose a Construction Method
Several construction methods are available for tiny houses, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
* Stick-built: This traditional method involves building the house frame from individual pieces of lumber, offering flexibility in design and customization.
* Modular: Modular construction involves building prefabricated sections of the house off-site and assembling them on the building site. This method can be faster and more cost-effective.
* Trailer-based: Trailer-based tiny houses are built on a trailer chassis, making them easily transportable. This option is ideal for those who desire mobility.
Select Materials
Choosing the right materials is essential for durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetics.
* Exterior: Consider using durable and weather-resistant materials for the exterior, such as cedar siding, fiber cement board, or metal panels.
* Interior: Select interior materials that are lightweight, durable, and aesthetically pleasing. Options include wood, bamboo, or recycled materials.
* Insulation: Adequate insulation is crucial for thermal comfort and energy efficiency. Consider using spray foam insulation, fiberglass batts, or cellulose insulation.
Determine Budget and Financing
Building a tiny house can be a cost-effective option, but it’s essential to have a realistic budget.
* Construction Costs: The cost of building a tiny house can vary depending on the size, materials, and construction method.
* Land Costs: If you plan to build on a lot, factor in the cost of land acquisition.
* Financing Options: Explore financing options like personal loans, home equity loans, or specialized tiny house financing programs.
Obtain Permits and Approvals
Building regulations vary from location to location, so obtaining the necessary permits and approvals is crucial.
* Zoning Regulations: Check local zoning regulations to ensure that tiny houses are permitted in your desired location.
* Building Codes: Your tiny house must meet local building codes and safety standards.
* Utility Connections: Secure permits and approvals for utility connections, such as water, sewer, and electricity.
Building the Tiny House: How To Build A 2 Bedroom Tiny House

With the planning and design phase complete, it’s time to bring your tiny house vision to life. Building a tiny house requires careful consideration of space constraints and a methodical approach to construction. This section will guide you through the process, from framing the structure to adding finishing touches.
Constructing the Frame and Foundation
A strong foundation is crucial for any structure, especially a tiny house that may be moved or transported. The foundation should be level and capable of supporting the weight of the house. Consider these steps for building the frame and foundation:
- Choose the Foundation Type: Tiny houses often use a variety of foundation types, including concrete piers, cinder blocks, or a simple trailer frame. The best option depends on your budget, local building codes, and the intended location of your tiny house.
- Prepare the Site: Clear the site of debris and vegetation. Level the ground using a laser level or a spirit level to ensure a stable foundation. If using a trailer frame, ensure it is properly positioned and secured.
- Construct the Foundation: Install the chosen foundation type according to local building codes. For concrete piers, excavate holes, pour concrete, and allow it to cure. For cinder blocks, stack them on a level surface, ensuring stability with mortar.
- Build the Frame: The frame of a tiny house is typically constructed using lumber, such as 2x4s or 2x6s. Use a framing square to ensure precise angles and a level to check for plumbness. Follow the pre-designed plans to create the walls, floor, and roof.
- Sheathing and Insulation: Once the frame is complete, apply sheathing to the exterior walls and roof. Sheathing provides structural support and a surface for siding or roofing materials. Install insulation to improve energy efficiency and create a comfortable living space.
Installing Plumbing and Electrical Systems
Efficiently integrating plumbing and electrical systems in a tiny house is essential. Space constraints necessitate careful planning and the use of compact fixtures and appliances.
- Plan the Layout: Before installation, carefully plan the location of sinks, toilets, showers, and electrical outlets. Consider the flow of water and electrical lines to minimize wasted space.
- Install Plumbing: Use PEX or copper pipes for water supply and drainage. Install a water heater and a septic system if necessary. Consider using a low-flow showerhead and toilet to conserve water.
- Install Electrical Wiring: Install electrical wiring according to local building codes. Use compact electrical fixtures and appliances to save space. Consider installing a solar panel system for off-grid living.
Installing Windows and Doors
Windows and doors play a crucial role in a tiny house, providing natural light, ventilation, and security. Choosing energy-efficient windows and doors can significantly improve the comfort and sustainability of your tiny house.
- Select Windows and Doors: Choose windows and doors that are energy-efficient, durable, and aesthetically pleasing. Consider double-paned windows and insulated doors to reduce heat loss and gain.
- Install Windows and Doors: Install windows and doors according to manufacturer instructions. Ensure proper flashing and sealing to prevent water infiltration. Install security features like locks and deadbolts for safety.
Creating the Interior Layout, How to build a 2 bedroom tiny house
The interior layout of a tiny house is critical for maximizing functionality and comfort. Creating a cohesive and efficient layout requires careful planning and creative design.
- Design the Layout: Consider the layout of the kitchen, bathroom, bedroom, and living area. Designate specific areas for storage and ensure that traffic flow is efficient. Use multi-functional furniture and appliances to maximize space.
- Build Interior Walls: Build interior walls using drywall, plywood, or other materials that meet your budget and aesthetic preferences. Install insulation to reduce noise and improve thermal efficiency.
- Install Interior Finishes: Install flooring, countertops, and cabinets. Consider using light-colored materials to create a sense of spaciousness. Choose durable and easy-to-clean materials for high-traffic areas.
Adding Finishing Touches
The finishing touches are what truly personalize your tiny house and create a warm and inviting atmosphere. From paint colors to furniture, these details make your tiny house unique.
- Paint the Interior and Exterior: Choose paint colors that complement your design aesthetic and create a desired ambiance. Consider using light colors to brighten the space. Use exterior paint that is durable and weather-resistant.
- Install Flooring: Choose flooring materials that are durable, easy to clean, and aesthetically pleasing. Consider using laminate flooring, hardwood, or tile. Install a rug in the living area to add warmth and comfort.
- Add Lighting and Fixtures: Install lighting fixtures that provide adequate illumination and enhance the overall ambiance. Choose light fixtures that are energy-efficient and complement your design aesthetic. Consider installing dimmer switches to adjust lighting levels.
- Decorate and Furnish: Add decorative touches, such as artwork, plants, and throws. Choose furniture that is multi-functional and complements the size and style of your tiny house.
Living in a Tiny House
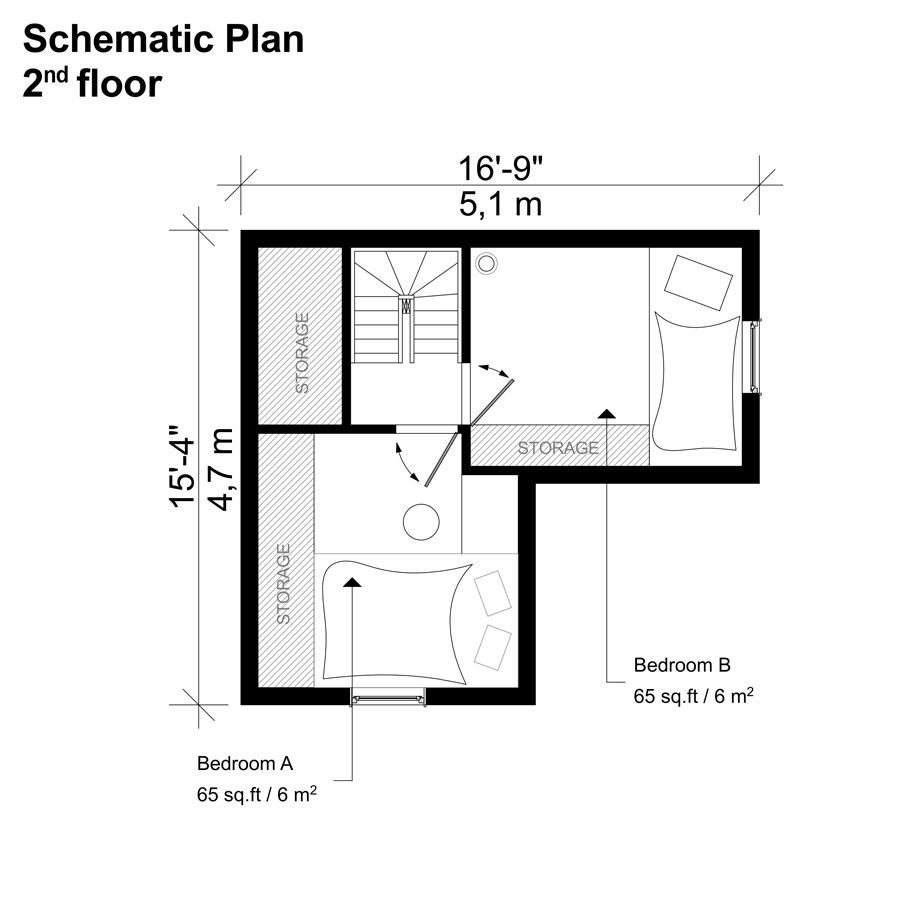
Living in a tiny house presents a unique lifestyle characterized by minimalism, intentional living, and a focus on sustainability. This approach offers a departure from traditional housing, with both advantages and challenges to consider.
Benefits of Living in a Tiny House
Living in a tiny house offers a range of benefits, primarily centered around financial savings, environmental consciousness, and a simplified lifestyle.
- Reduced Housing Costs: Tiny houses typically cost significantly less to build and purchase than traditional homes, leading to lower mortgage payments or rent. This financial freedom can allow for greater financial flexibility and the pursuit of other life goals.
- Lower Utility Bills: The smaller footprint of a tiny house results in reduced energy consumption for heating, cooling, and water usage, leading to lower utility bills.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Tiny houses require fewer resources to build and maintain, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. The smaller size also reduces the need for land and resources, contributing to a more sustainable lifestyle.
- Simplified Lifestyle: Living in a tiny house often encourages a minimalist approach, leading to less clutter and a more intentional way of living. This can free up time and energy for pursuing passions and experiences.
Challenges of Living in a Tiny House
While tiny houses offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges to consider:
- Limited Space: The most significant challenge is the limited space, requiring careful planning and organization to maximize functionality.
- Lack of Privacy: Depending on the design and location, tiny houses may offer less privacy than traditional homes, particularly for families or individuals who value personal space.
- Accessibility: Tiny houses can be challenging for individuals with mobility limitations due to their smaller size and often limited accessibility features.
- Social Acceptance: Tiny houses may face challenges in terms of zoning regulations and community acceptance, particularly in areas with traditional housing norms.
Maximizing Space in a Tiny House
Maximizing space in a tiny house is essential for creating a comfortable and functional living environment.
- Multi-Functional Furniture: Utilize furniture that serves multiple purposes, such as a sofa bed or a dining table that can double as a workspace.
- Vertical Storage: Maximize vertical space by using shelves, wall-mounted organizers, and storage bins to store items efficiently.
- Hidden Storage: Incorporate hidden storage solutions, such as drawers built into steps or under beds, to keep items out of sight.
- Minimalism: Embrace a minimalist approach by decluttering regularly and only keeping items that are essential and bring joy.
Sustainable Living Practices in a Tiny House
Living in a tiny house presents an opportunity to adopt sustainable practices that minimize environmental impact:
- Energy Efficiency: Install energy-efficient appliances, use LED lighting, and consider solar panels to reduce energy consumption.
- Water Conservation: Install low-flow showerheads, toilets, and faucets to conserve water. Consider rainwater harvesting systems for watering plants and outdoor use.
- Composting: Compost food scraps and yard waste to reduce landfill waste and create nutrient-rich soil for gardening.
- Local Sourcing: Support local farmers and businesses by sourcing food and other goods from nearby sources, reducing transportation emissions.
Examples of Successful Tiny House Living
Numerous individuals and families have successfully embraced the tiny house lifestyle, demonstrating its feasibility and benefits.
- The Tiny House Blog: This blog, maintained by a couple who built and live in a tiny house, documents their journey, sharing practical tips, design ideas, and inspiring stories about tiny house living.
- The Tiny House Movement: This global movement has gained significant traction, with communities and events dedicated to promoting tiny houses and sustainable living.
- Tiny House Communities: Several tiny house communities have emerged, providing a sense of belonging and shared values for those who choose to live in small spaces.
How to build a 2 bedroom tiny house – Building a two-bedroom tiny house requires careful planning and resourcefulness, just as finding the right space for your journey does. Whether you’re seeking a cozy haven for yourself or a shared sanctuary with a roommate, consider the possibilities that lie beyond the traditional home.
A 2 bedroom student house in York could offer a temporary haven while you navigate your studies, much like a tiny house provides a space for growth and reflection. Both approaches prioritize functionality and resourcefulness, encouraging us to find meaning and purpose within the confines of our chosen space.
Building a 2-bedroom tiny house can be a journey of mindful simplicity, allowing you to shed unnecessary material possessions and embrace a life of intentional living. Consider the environmental impact of your choices, such as energy efficiency. For instance, you might be surprised to learn that the average electric bill for a 5-bedroom house can be significantly higher than a smaller dwelling.
By minimizing your footprint, you can create a space that fosters peace and connection with nature, while also contributing to a more sustainable future.